
My first degree was in mathematics at the University of Cambridge. After taking a postgraduate diploma in computing, I became a graduate student at the LMB. Most of my career has been at the LMB, where I was Joint Head of the Structural Studies Division from 1994 to 2005.
In my early research, I developed mathematical techniques for protein crystallography, including the translation function and the fast rotation function, used in molecular replacement for solving protein structures. I then developed methods for image processing in electron microscopy, in particular for making three-dimensional maps from the two-dimensional projected images provided by the micrographs.
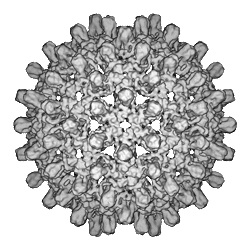
I have worked on the structures of various macromolecular assemblies, including clathrin-coated vesicles, muscle filaments and viruses in particular. The most significant of these was human hepatitis B virus, or hepB. We solved the structure of the bacterially expressed hepB core particle at 7.4 Å resolution, showing a largely α-helical fold, to which we assigned an amino acid numbering. This was the first structure solved in this detail by single particle cryo-EM, later confirmed by X-ray crystallography. We then studied the cores of hepB virus particles extracted from infected blood and, based on differences between the two types of core, proposed a model for the signalling of maturation of the core during intracellular envelopment of the virus.
The other main area of my work has focussed on the abnormal filaments that form in the brain in many neurodegenerative diseases. In Alzheimer’s disease these form intracellular tangles and extracellular plaques. The tangles are formed of paired helical and straight filaments made of tau protein. My early morphological analysis showed that both were formed from transversely arranged C-shaped subunits but with different packings. It was very exciting when developments in cryo-EM by Sjors Scheres allowed the determination of the atomic structures of the filaments, confirming in detail my earlier findings.
I was elected a member of EMBO in 1985, a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1993 and a Fellow of the Academy of Medical Sciences in 2007. I am a Fellow Emeritus at Peterhouse, University of Cambridge.