Ingo Greger
AMPA receptor biogenesis, structure and function

Information transfer and storage in the nervous system occur at synapses, where presynaptic signals in the form of action potential trains are interpreted by postsynaptic receptors. Receptors responding to the ubiquitous neurotransmitter L-glutamate are central to brain function and enable learning and memory processes. AMPA-type receptors form a highly versatile signalling system, comprising around 30 components, which is capable of decoding diverse action potential patterns and enables the storage of information through synaptic plasticity mechanisms.
Our core aim is to understand how AMPA receptor complexes transmit and store information, and we use a variety of approaches to do this. We combine electron cryomicroscopy and patch-clamp electrophysiology to study how the organisation of physiologically relevant receptor complexes enables the decoding of different neuronal activity patterns at model synapses. We also develop small-molecule ligands capable of modulating specific AMPA receptor subtypes, towards the generation of selective therapeutics.
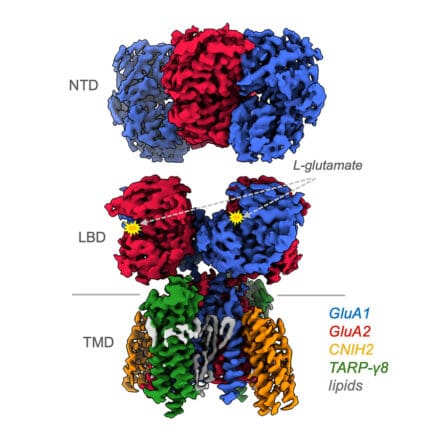
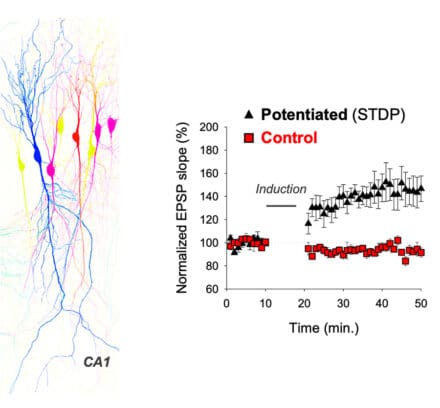
We build on this information to unravel AMPA receptor operation at synapses. We ask how receptors of different subunit compositions are selectively targeted to and anchored at synapses undergoing learning. To this end, we use a combination of brain slice electrophysiology as well as super-resolution light and electron microscopy approaches.