Roger Williams
Structural studies of phosphoinositide signalling and intracellular sorting

Eukaryotic cells have evolved mechanisms to respond to environmental stress that are tempered by signals from surrounding cells in multicellular organisms. Our research programme investigates the mechanisms whereby these cellular signals regulate mammalian cells. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks) modify lipid membranes to produce second messengers and sorting signals that are important for cellular responses to environmental cues. PI3Ks are part of a superfamily of kinases that also includes the PI3K-related protein kinases (PIKKs). We study the structures, dynamics and functions of the PI3K superfamily and related pathways in cellular signalling, protein sorting, nutrition, organelle biogenesis and nerve regeneration. In addition to understanding PI3Ks and PIKKs in these processes, we are selecting and designing small molecules that exploit unique dynamics of these enzymes to activate them, for example, the PI3Kalpha activator 1938 that speeds nerve growth.
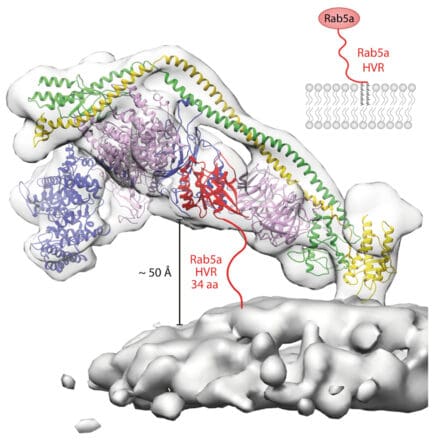
Our work on multiprotein complexes of PI3K-like enzymes includes class I PI3Ks activated by receptor tyrosine kinases and GPCRs, the primordial class III PI3K (VPS34) complexes present in all eukaryotes, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM). We use electron cryomicroscopy/tomography (cryo-EM/cryo-ET) hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS), enzyme kinetic measurements, and computational simulations to marry structures with dynamics. With cryo-EM, we can visualise how these complexes assemble on and are regulated by cellular membranes.