The complexity of eukaryotic life forms is driven by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), which transcribes all protein-coding genes and thousands of non-coding RNA loci in a context-specific manner. The Tufegdžić Vidaković group uses a combination of genome-wide, biochemical and cell biology tools to study the transcription process.
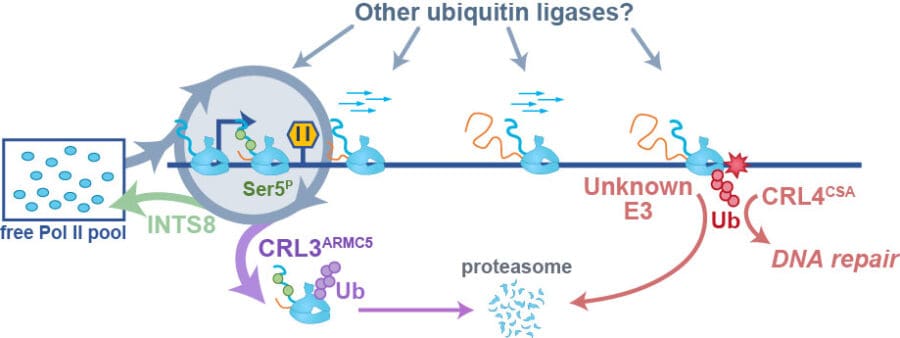
For decades it was believed that Pol II activity was strictly regulated at the first steps of gene expression: transcription initiation and pausing. Recent studies demonstrate that additional checkpoints exist and control gene expression output in a rate-limiting way. Our group recently discovered one such checkpoint, whereby CRL3ARMC5 ubiquitin ligase and Integrator phosphatase work in parallel to survey the quality and quantity of Pol II molecules at the beginnings of genes, before they are licensed to proceed into the gene body. Our work sheds light on the power of ubiquitin-mediated Pol II regulation and we are now focussing on discovering other ubiquitylation pathways that regulate Pol II.
Many human genes are very long, and transcribing a single RNA copy takes Pol II hours. How elongating Pol II is regulated on its journey across the genes remains poorly understood. Obstacles such as DNA damage cause elongating Pol II to stall and block gene expression. We investigate the mechanisms that regulate elongating Pol II and resolve transcription when Pol II stalls.