Albert Cardona
Experimental and comparative connectomics

Animals integrate multiple sensory inputs with memories to select an appropriate behavioural response. Being modularly organised, the output of local signal processing within a brain module is but one of the inputs into another. Hence, to understand how the brain works, we must first map its complete synaptic wiring diagram, the connectome. Then, together with observations of neural activity and behaviour, computational models can capture the known circuit dynamics to tell us how neural circuits implement behaviour.
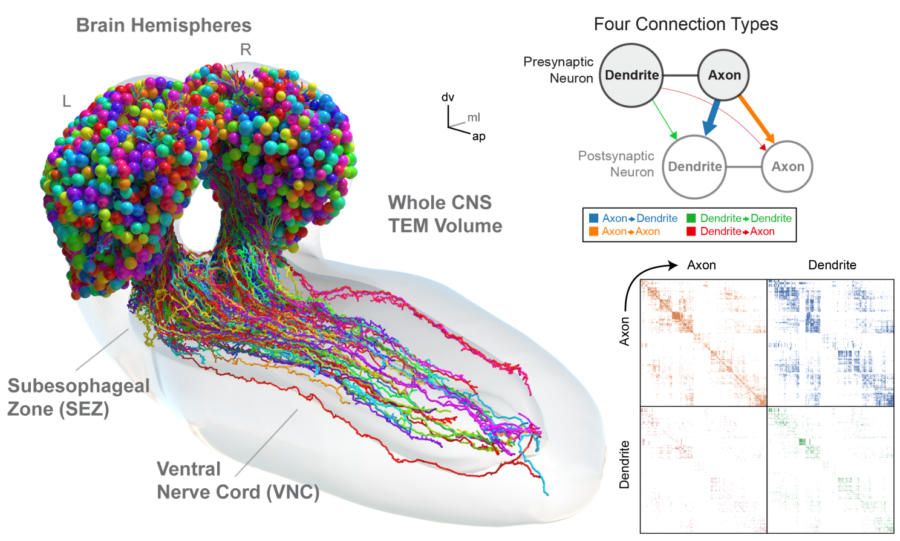
We are interested in studying connectomes of complete nervous systems, or at the very least of complete brains. We image them with dense labelling techniques such as volume electron microscopy (eFIB-SEM, GridTape TEM and others), to comprehensibly map their complete connectomes with both computer-assisted and automated techniques. We develop computational methods using computer vision and machine learning techniques, and implement them as open source software to assemble continuous volumes, identify synapses and segment neuronal arbors (Fiji/TrakEM2, CATMAID, CATENA). Through cross-modal registration, we bridge the resolution gap to relate neuronal activity imaged with light-sheet microscopes to EM-mapped connectomes. With these data, we formulate neural circuit models to study brain function in silico, dissecting the contribution to behaviour across the scales, from brain modules to circuit motifs and sub-neuron interactions such as axo-axonic synapses.
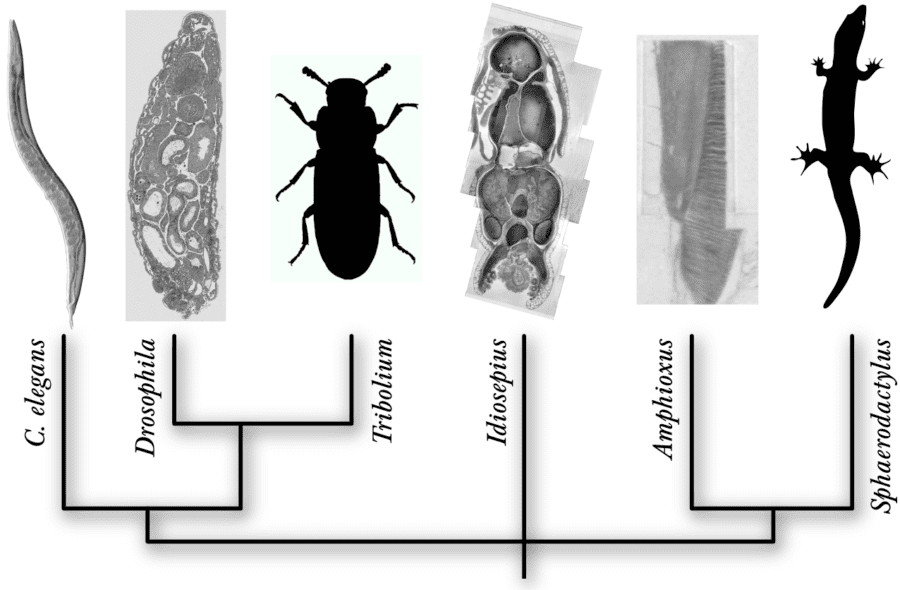
While our primary focus is on the larval fruit fly, Drosophila, where genetic techniques, prior knowledge, reduced dimensions and numerically-reduced complexity offer outstanding experimental accessibility and reproducibility, we also study the nervous system of pygmy squids (Idiosepius sp.), simple chordates such as the lancelet (Amphioxus sp.), the flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum), small lizards (Sphaerodactylus sp.) and others. Particular emphasis is given to neural circuits for learning and memory, and for vision and olfaction, in the context of both the wild-type and disease models.