Harvey McMahon
Membrane curvature as an organising principle for eukaryotic cell biology

Neurons have a variety of cell shapes that are adapted to function in interconnected neural circuits. We initially focussed on how membrane shapes are generated, and in particular how local membrane deformations are formed, describing membrane-bending motifs and domains (for example, the BAR-superfamily) that detect and stabilise various curvatures.
The investigation of curvature brings us into many areas of neurobiology and cell biology by taking a fresh look at physiological processes like exocytosis, endocytosis and membrane trafficking. We are currently investigating the implications of membrane insertion by α-synuclein and disease-associated mutants for Parkinson’s.
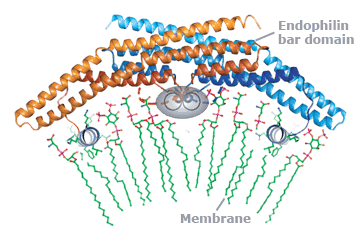
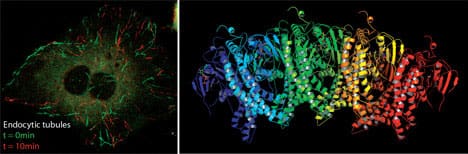
This approach has allowed us to ascribe novel cell biological functions to proteins, such as the mechanistic effect of synaptotagmin in membrane fusion, and the role of endophilin in a non-clathrin pathway of endocytosis, and provides a more molecular view of how these processes work.
The most recent pathway we described, and continue to work on, is Aggregation-Dependent Endocytosis (ADE). This pathway is important for plasma membrane proteostasis and for removing protein aggregates from the cell surface. Indeed, aggregates of various proteins in the brain are neurotoxic, so a molecular understanding of this pathway is of fundamental importance.